In an increasingly digital world, accessibility has become a pivotal focus for technology developers, particularly for mobile platforms like Android. As smartphones integrate deeper into daily life, ensuring that everyone—regardless of ability—can access their features is essential. Android’s commitment to accessibility is not just a technical enhancement; it is a powerful transformation that touches lives and reshapes user experiences.
The Importance of Accessibility
Accessibility in technology means creating products and services that everyone can use, including those with disabilities. This can include visual impairments, hearing loss, motor difficulties, or cognitive challenges. According to the World Health Organization, over a billion people worldwide experience some form of disability. With such a significant portion of the population potentially facing barriers in using digital tools, the importance of inclusive design is clear.
Android’s Accessibility Features
Android’s accessibility framework provides a wide range of features designed to enhance usability for all users:
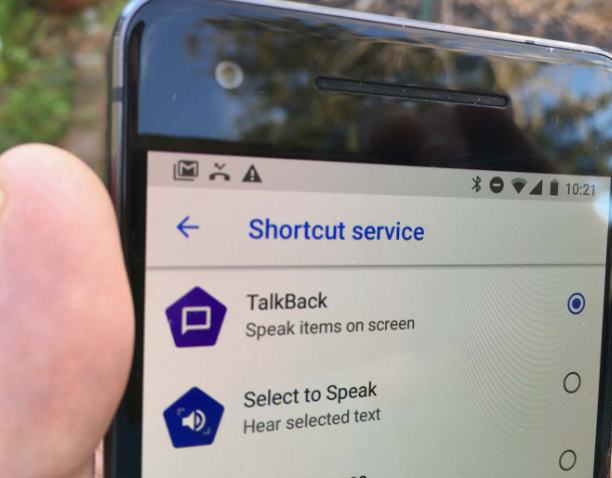
1. TalkBack: Empowering the Visually Impaired
TalkBack is a screen reader that allows visually impaired users to interact with their devices through spoken feedback. By providing auditory descriptions of what’s on the screen, TalkBack enables users to navigate apps, read messages, and even browse the web, transforming their relationship with technology.
2. Voice Access: Hands-Free Control
For individuals with motor impairments, Voice Access offers a revolutionary way to control their devices. This feature allows users to navigate their Android devices using voice commands, providing a hands-free experience that enhances independence and usability.
3. Accessibility Menu: Simplifying Navigation
The Accessibility Menu provides an easy-to-use interface for those who may struggle with traditional touch controls. Users can access common functions, such as adjusting volume or taking screenshots, with just a few taps, streamlining the navigation process and reducing frustration.
4. Switch Access: Tailored Interaction
Switch Access allows users with limited mobility to interact with their devices using switches or adaptive devices. This customizable approach means users can create a setup that works best for them, providing greater control and personalization.
5. Live Transcribe: Bridging Communication Gaps
For the deaf and hard-of-hearing community, Live Transcribe converts spoken language into text in real-time, facilitating conversations and making information accessible. This feature enhances social interactions, educational opportunities, and workplace inclusion.
The Impact on User Experience
The integration of these features into Android devices has a profound impact on user experience. By addressing diverse needs, Android enhances usability and empowers individuals. The result is not just an improved interaction with technology; it’s a sense of belonging and independence.
Empowerment Through Independence
When users can access their devices without assistance, it fosters a sense of empowerment. Individuals who may have previously felt excluded from the digital landscape can now participate fully. This empowerment extends beyond personal use, influencing social interactions, educational achievements, and professional opportunities.
Enhancing Communication
Effective communication is a cornerstone of social interaction. Android’s accessibility features break down barriers, allowing users to connect more easily with friends, family, and colleagues. This transformation is especially crucial in fostering inclusive environments, where everyone has the opportunity to engage.
Fostering Inclusivity in Society
By prioritizing accessibility, Android sets a precedent for inclusivity in technology. As more developers recognize the importance of creating accessible applications, the digital landscape evolves into a more welcoming space for all users. This shift not only benefits individuals with disabilities but also enriches the user experience for everyone.
The Road Ahead
As technology continues to advance, the need for robust accessibility features will only grow. Android’s ongoing commitment to innovation in this space is crucial. Future developments could see even more sophisticated tools that leverage artificial intelligence, machine learning, and augmented reality to further enhance accessibility.
In conclusion, Android’s approach to accessibility is more than just a set of features; it is a transformative movement that is changing lives. By making technology accessible, Android not only enhances the user experience but also promotes independence, communication, and inclusivity. As we move forward, the continued evolution of accessibility will play a critical role in shaping a more equitable digital future.




